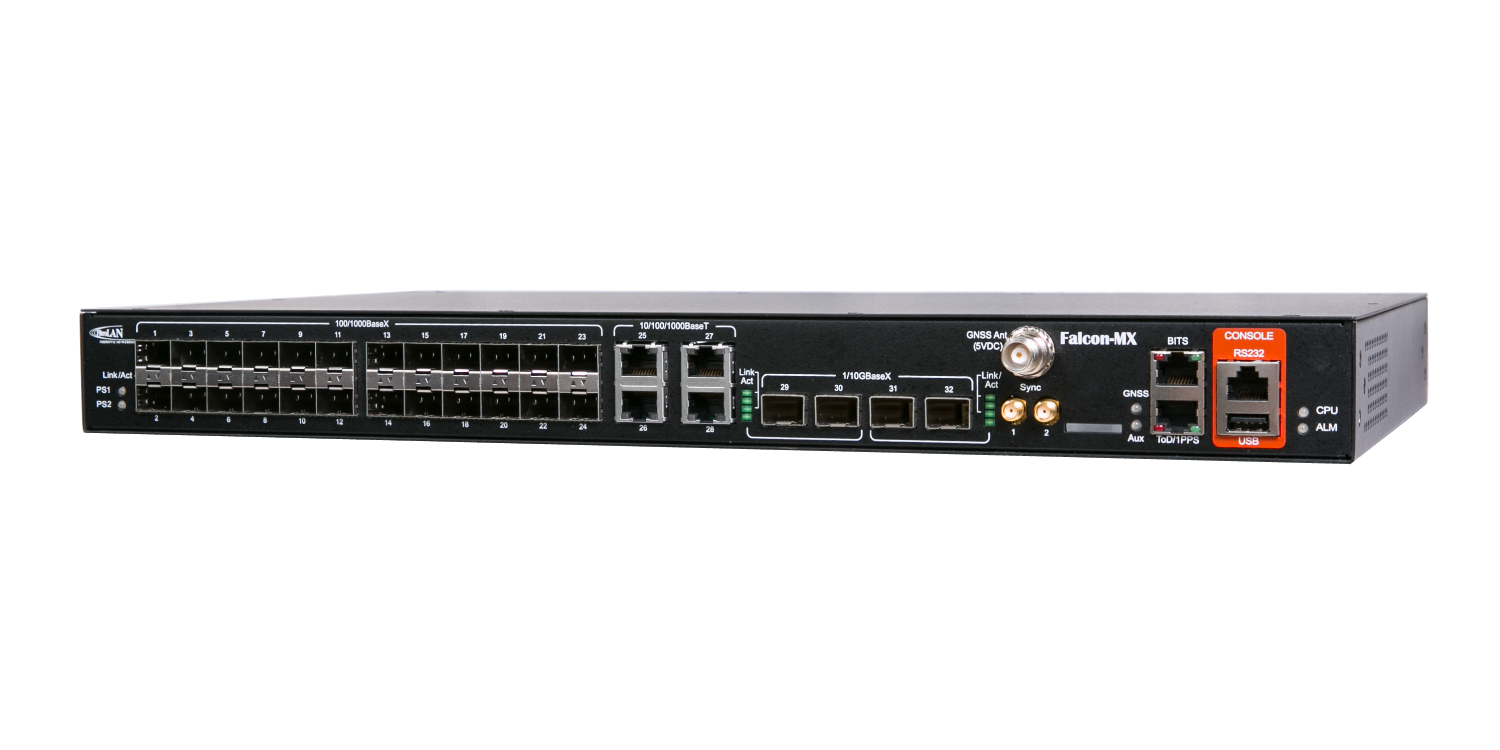
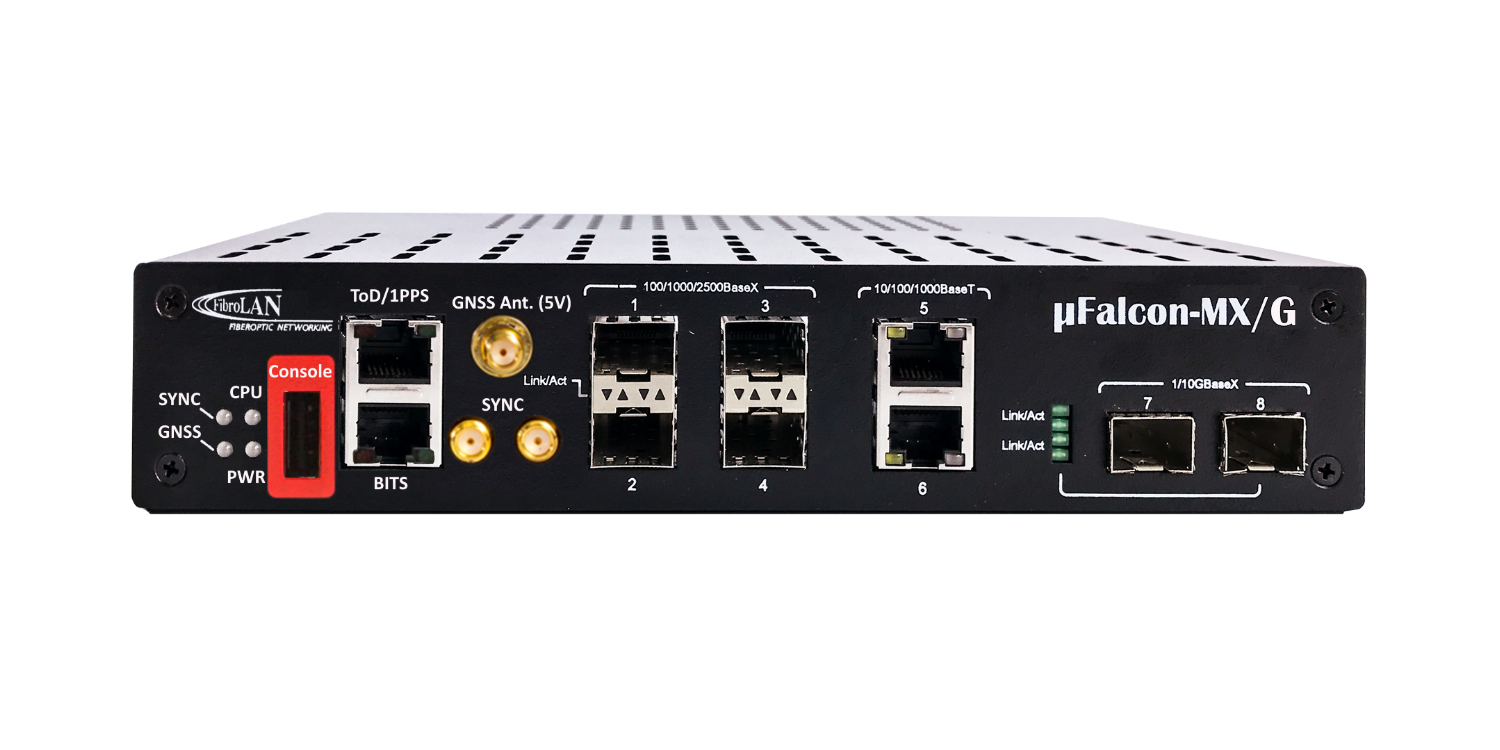
BITS Clock
Fibrolan’s GPS/GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) referenced BITS Clocks portfolio includes a wide offering that combines a high fan out models with exceptional functionality and flexibility.
To learn more about Fibrolan’s BITS Clock offering follow the links below:
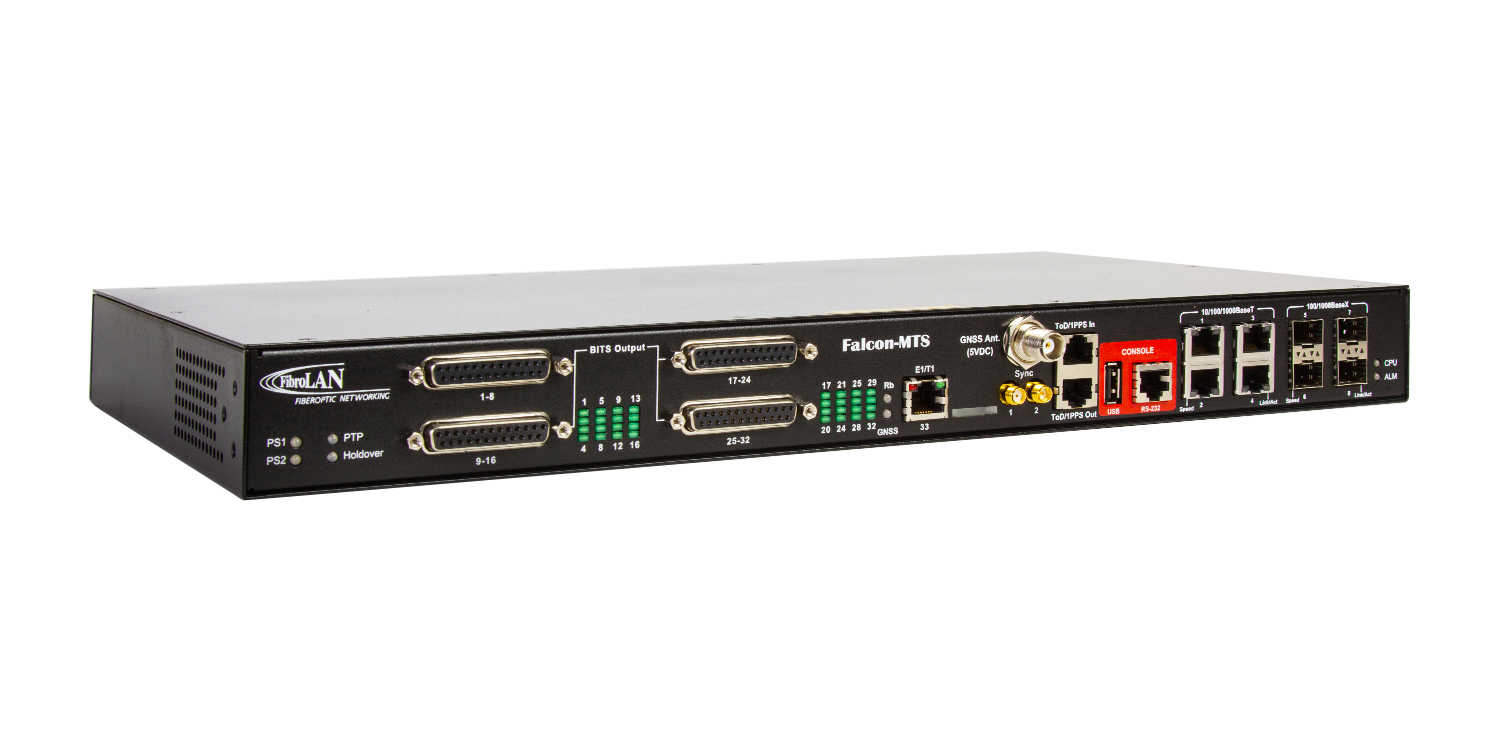 Falcon-MTS |
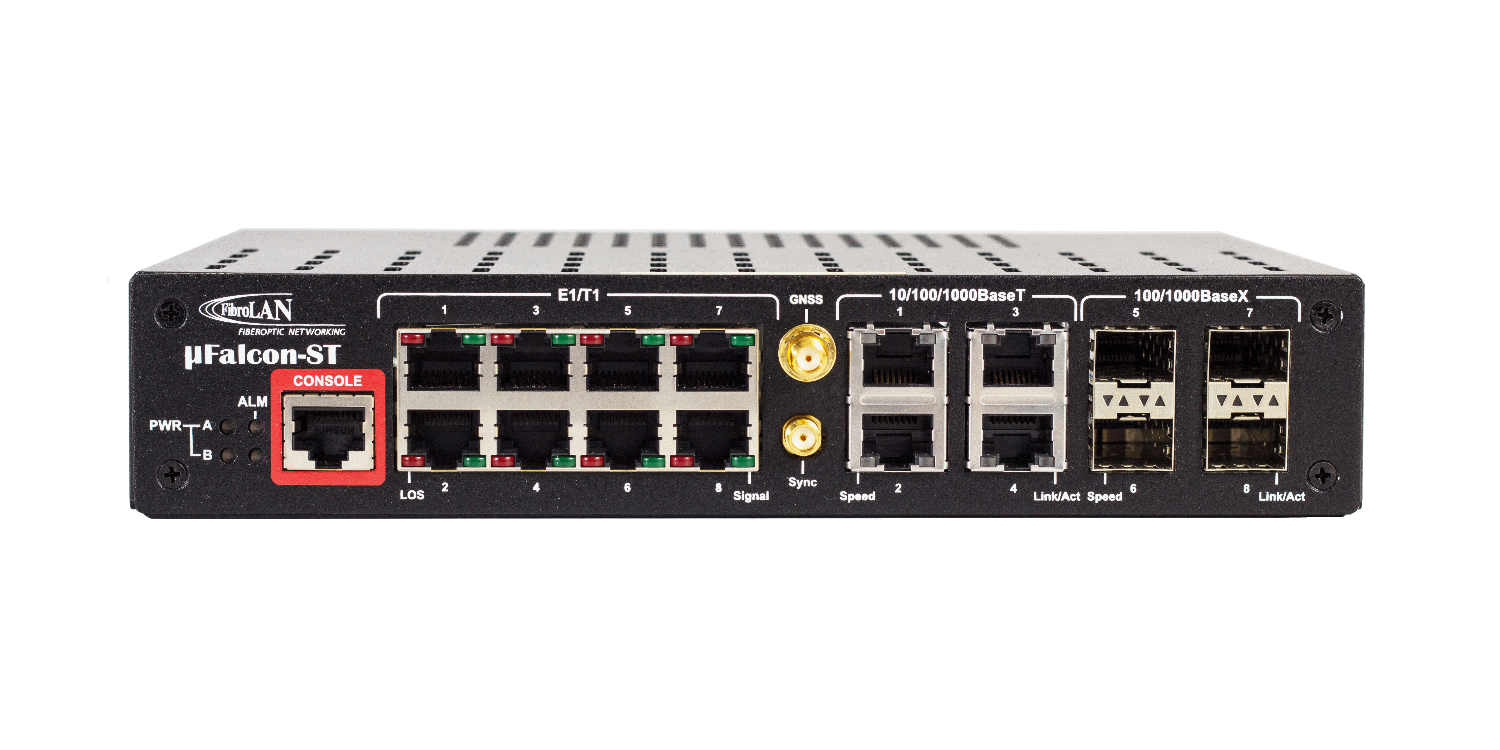 μFalcon-ST/G |
Building Integrated Timing Supply (BITS) is a synchronous Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) signal, used to synchronize communication systems and data networks. This type of signal is a highly reliable and stable source for propagating frequency over wide transmission networks. It does not, however, support phase or Time of Day (ToD) synchronization. These traits make a BITS Clock an ideal Timing source for legacy TDM networks (SONET/SDH), local business telephone exchange (VoIP and TDM PBXs), 2G and 3G mobile communication network and even aviation traffic control systems.
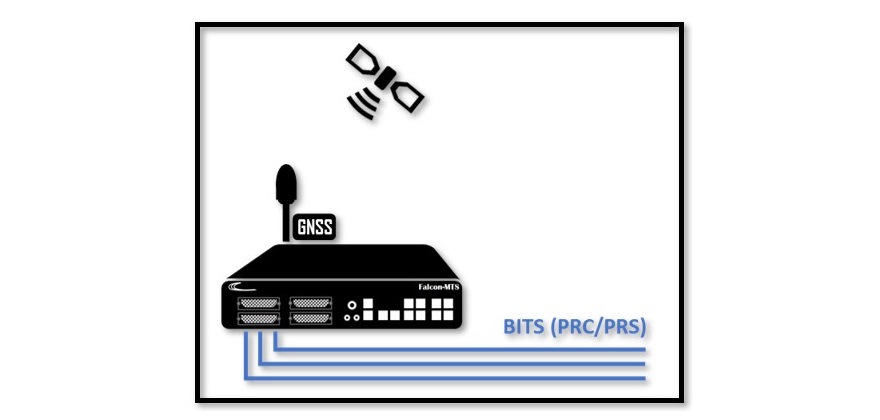
BITS Clock links are unidirectional by nature and transmit the clock signal from a Master clock or Office clock to relevant Network Elements. Network Elements can recover the clock directly from the line when terminating a service or continue transmitting it to Network Elements connected further down the chain.
BITS interfaces can support the following frequencies:
|
These signals cannot carry quality level indication of the source generating the Timing information. |
|
These signals can carry quality level indication of the timing source via the Synchronization Status Message (specified in ITU-T Recommendation G.704). |
Synchronization Status Message (SSM)
The purpose of the Synchronization Status Message (SSM) is to indicate the clock quality (stability, accuracy, etc.) of the Timing signal that is carrying it, in effort to assist the Network Elements to select the highest clock quality available to them. The messages are inherent in the Extended Super Frame (for T1) or Multiframe (E1). SSM messages announce the signal quality and source type or indicate that the Timing source has been compromised and the signal is not to be used (DNU).
Timing Loops
A Timing Loop occurs when two systems try to recover the clock signal from one another at the same time. Each of the devices operates as a slave trying to adjust its local clock to match the recovered clock coming from the other device. Such condition leads to an everlasting clock adjustment, without ever reaching a locked state, along with a high risk of driving local clocks out of operational range, rendering the system not able to deliver services. SSM messages serve yet another purpose in avoiding Timing Loops, by indicating which links should and should not be used as a Timing source.
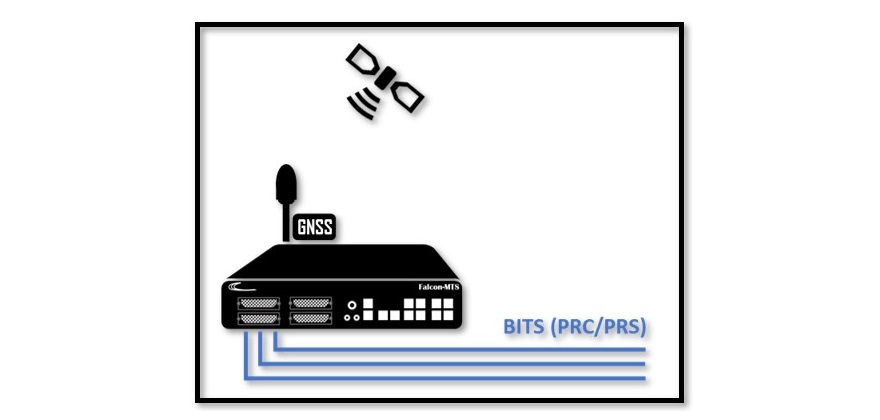
Falcon’s Flexible Design
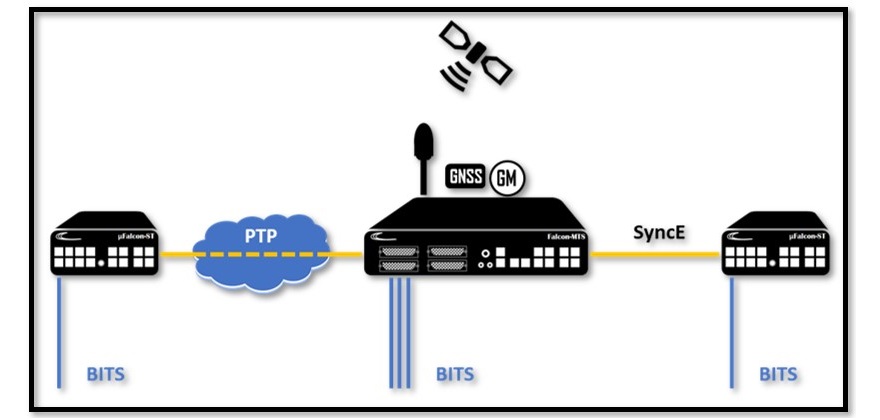
Fibrolan’s wide offering of Timing Grandmaster supports BITS interfaces on all models. It can provide a reliable Timing signal sourced by GNSS and backed up by a variety of secondary timing input signals such as PTP, SyncE, External (10MHz or 1PPS) or even a secondary BITS input of a different source.
Common Use Cases
Telephony
Whether they are legacy TDM based or newer VoIP, business telephone exchanges (PBX) require a timing source to properly originate and terminate phone calls to and from the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). While accuracy is important, such switches only require frequency synchronization to operate increasing the importance of high availability and reliability of the timing source service.
2G and 3G Mobile services
The older generation mobile networks (2G/3G) are still in service today in many countries around the world, whether to maintain service to a variety of existing legacy devices or as a fallback option. 2G and 3G base stations relies on BITS clock for synchronization and on TDM technology to carry voice services. Fibrolan’s µFalcon-ST/G can provide a solution for both requirements serving as an accurate and reliable Timing source while connecting the TDM lines over packet networks using Circuit Emulation Services (CES).
Aviation
Traffic control and aviation monitoring is a mission critical application that requires high level of accuracy and precision in execution, while maintaining utmost reliability and resiliency. For this purpose, different type of highly robust and reliable systems and equipment have been developed over the years. Many of these systems were designed when modern timing interfaces and protocols, such as PTP and SyncE, were not yet available and therefor rely on legacy BITS timing interfaces for synchronization.
Availability and Protection
Timing source is a mission critical requirement for many communication networks. Without it, data communication between network elements is disrupted. Therefore, protection mechanisms and redundancy layers are implemented to assure the Timing signal is constantly maintained.
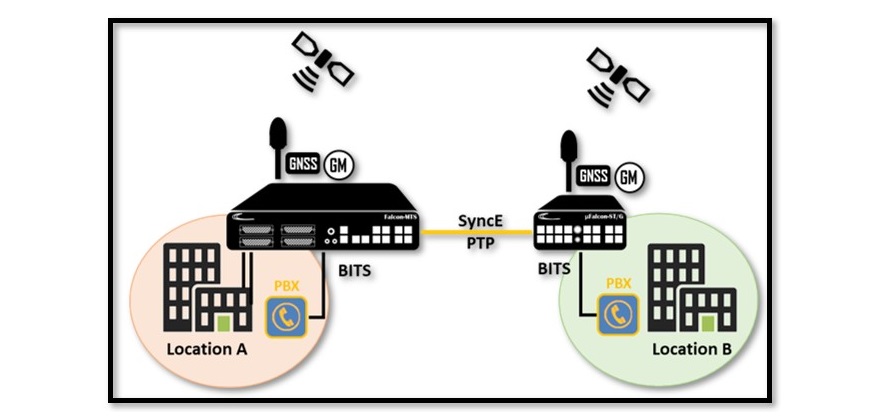
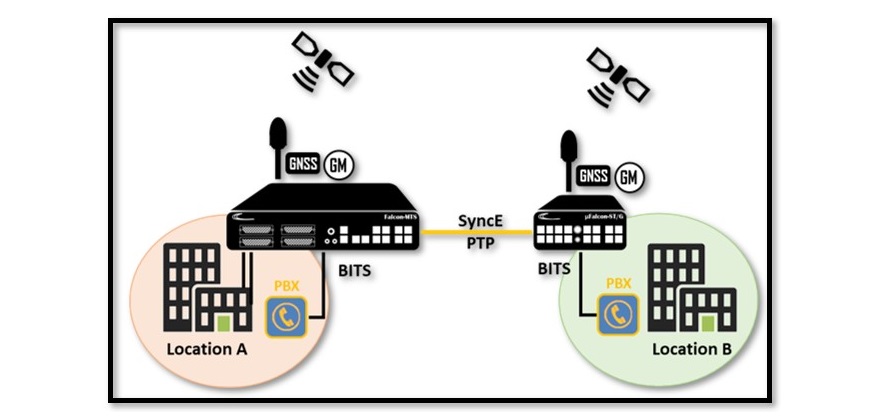
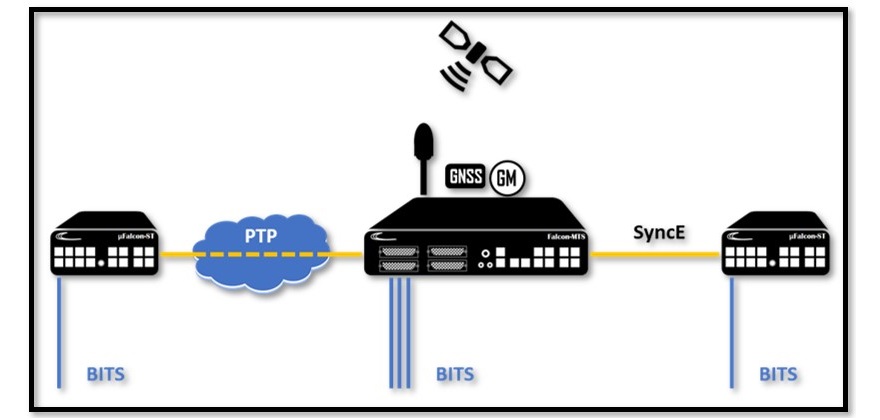
Mutual Redundancy
In order to increase the availability and reliability of the BITS clock signal delivered by the Falcon Grandmaster models, the Falcon Grandmasters are equipped with a unique redundant mode of operation called – Mutual Redundancy. This protection mechanism allows two or more Timing servers to lock on the GNSS signal as their primary Timing source and receive secondary source(s) from remotely located Falcon units via PTP and/or SyncE over a fiber connection. On any occasion of a failure with the GNNS signal the Timing system will automatically shift to one of the secondary sources.